How Do the Secondary Structures of Dna and Rna Differ
A set of pairs S b i b j that satisfy. Moreover they are the building blocks of genetic material of an organism.
Nucleotides Composition And Structure
No sharp turns The ends of each pair are separated by at least 4 intervening bases.
. RNA only has one strand but like DNA is made up of nucleotides. Watson-Crick S is a matching and each pair in S is a Watson-Crick pair. Secondary structure is the set of interactions between bases ie which parts of strands are bound to each other.
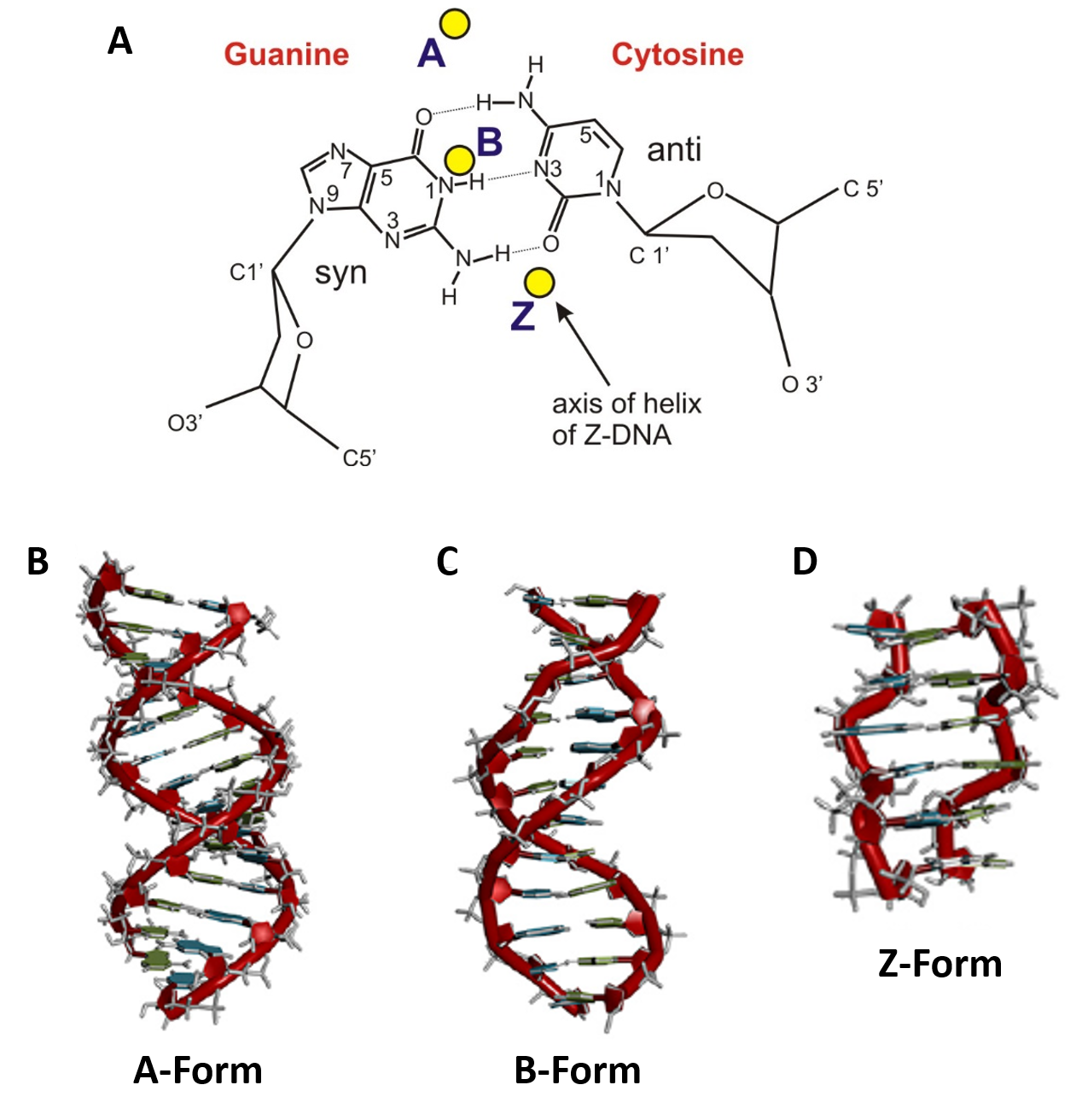
DNA is a much longer polymer than RNA. The regions of the secondary structure do not have to form between sequences that are close together. The secondary structure of DNA consists of mainly B-form double helix while the secondary structure of RNA consists of short regions of A-form of a double helix.
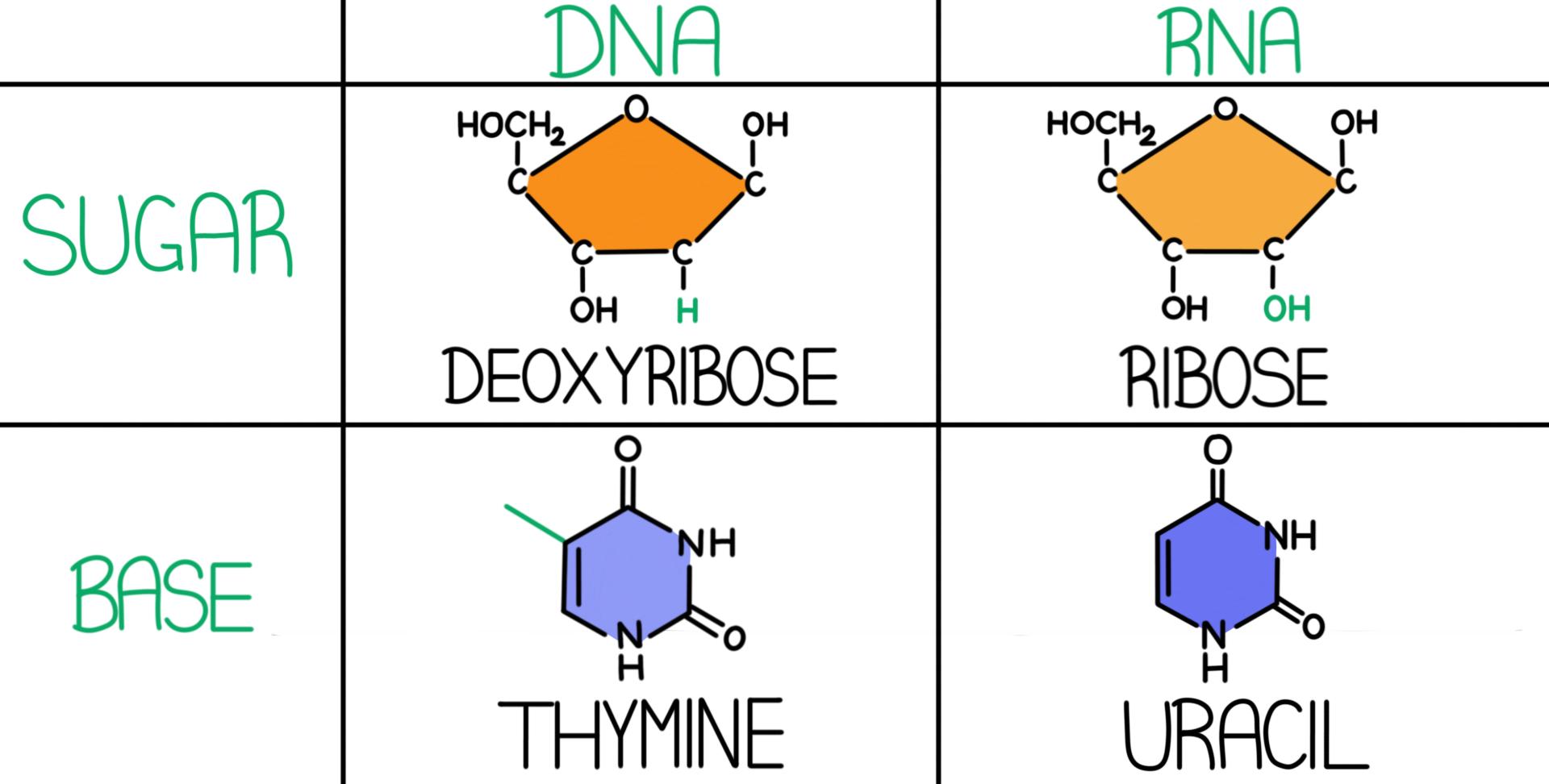
Non-crossing If b i b. The difference between deoxyribose and ribose is that deoxyribose has a hydrogen -H attached to the second 2 carbon of the sugar ring while ribose has a hydroxyl group -OH attached to this carbon. -secondary structure is the 3-dimensional conformation of the backbone.
RNA is only a single strand and comes in a variety of shapes. These two processes are descibed in the theory of compensatory substitutions section. The base- pairing that occurs in RNA is all through regions of self-complementarity.
D Only RNA and not DNA has a primary structure. DNA and RNA are different from each other in several ways. Non Watson-Crick base pairing where guanine pairs with uracil is allowed in RNA but not in DNA.
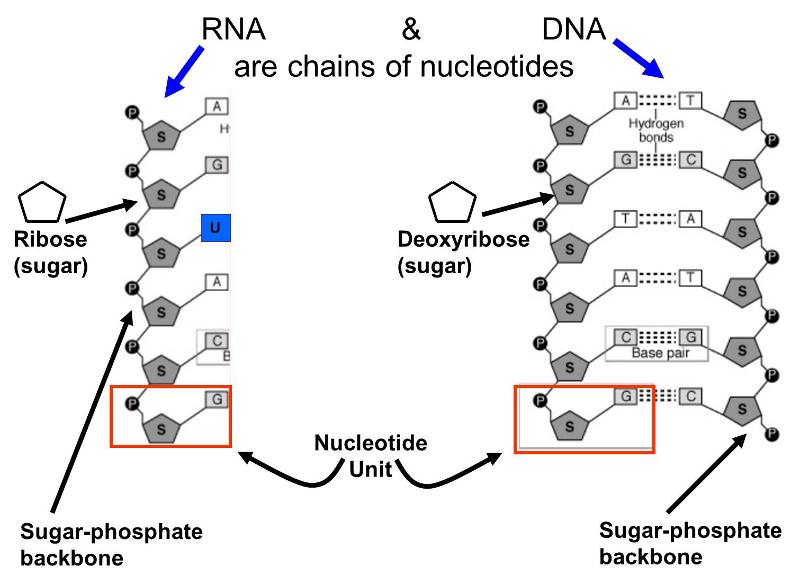
DNA uses the sugar deoxyribose while RNA uses the sugar ribose. The basepairing of complementary nucleotides gives the secondary structure of a nucleic acid. The fundamental characteristic of DNAs secondary structure is that it consists of two polynucleotide strands wound around each other known as the double helix.
DNA consists of two nucleotide strands and RNA consists of one that often folds on itself. If b i b j S then i j - 4. RNA Secondary Structure Secondary structure.
DNA has a few major differences from RNA. The sequence of bases in the nucleic acid chain gives the primary structure of DNA or RNA. Two significant differences between DNA and RNA 1 Sugar in the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA is deoxyribose and of RNA is ribose 2 DNA contains the.
The secondary structure is left unchanged when complementary substitutions occur in the DNA gene coding for the RNA molecule. A-U U-A C-G or G-C. DNAs sugar is deoxyribose while RNAs sugar is.
Secondary Structure of Deoxyribonucleic Acids. Generally mRNA secondary structures like hairpin loop stem will cause interference with the translation of protein. The key difference between DNA and RNA structure is that the DNA structure is a double helix composed of two complementary strands while RNA structure is single-stranded.
The sugar-phosphate linkages are on the outside of the helix and the bases are stacked in the interior of the molecule as shown in the figure. DNAs secondary structure tends to be a double helix while RNA often has intramolecular bondind that forms things like hairpin loops etc. For example the cloverleaf.
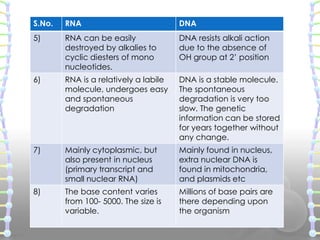
-primary structure of nucleic acids is the order of bases in the polynucleotide sequence. DNA is almost always restricted to the interior of the nucleus but various forms of RNA can enter and leave the nucleus. Some observations made on deoxyribonucleic acids in solution suggested that DNA molecules as they could be extracted from cells had structural characteristics different from those expected in molecules having only the primary structure we just described.
This three-dimensional arrangement is called the tertiary structure of RNA and it can be very. They are comprised of nucleotide chains linked via. DNA is a double helix made of two joined strands forming a structure like a twisted ladder.
Explain what it means when we say the two strands of the DNA helix are antiparallel. Nucleic acids have a primary secondary and tertiary structure analogous to the classification of protein structure. RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands.
The secondary structures of biological DNAs and RNAs tend to be different. Describe the secondary structure of DNA. Biological DNA mostly exists as fully base paired double helices while biological RNA is single stranded and often forms complex and intricate base-pairing interactions due to its increased ability to form hydrogen bonds stemming from the extra hydroxyl group in the ribose sugar.
How do DNA and RNA differ. Answer -In RNA secondary structure is represented by a list of the nucleotide bases paired by hydrogen bonding within its nucleotide sequence. In a doublestranded DNA or RNA this refers to the WatsonCrick pairing of complementary strands.
The process can be a single step process double substitution or a two step process two single substitutions. What is the difference in their primary structure. Stacking these base p.
Common Secondary Structures of RNA The main difference between the three-dimensional structures of DNA and RNA is that in RNA the three-dimensional structure is single-stranded. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose but RNA has ribose in the same position. Given a DNA or RNA sequence the.
B Adenine pairs with thymine in DNA while adenine pairs with uracil in RNA. Or the ordered arrangement of nucleic acid. What type of bonds connect the nitrogenous bases of the complementary DNA strands.
How do the secondary structures of DNA and RNA differ. C Guanine pairs with cytosine in DNA while guanine pairs with adenine in RNA. View the full answer.
If 14C-labeled uracil is added to the growth medium of cells what macromolecules will be labeled. The difference in the sugars gives rise to differences in their secondary and tertiary structures. In a singlestranded RNA or DNA the intramolecular base pairs between complementary base pairs determines the secondary structure of the molecule.
What is the base pairing rule in DNA structure. On the contrary after heating the DNA molecules behaved like. A DNA contains the sugar ribose while RNA contains the sugar deoxyribose.
Nucleic acids are macromolecules or biopolymers. How do the structures of RNA and DNA differ. RNA sometimes forms a secondary double helix structure but only intermittently.

Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
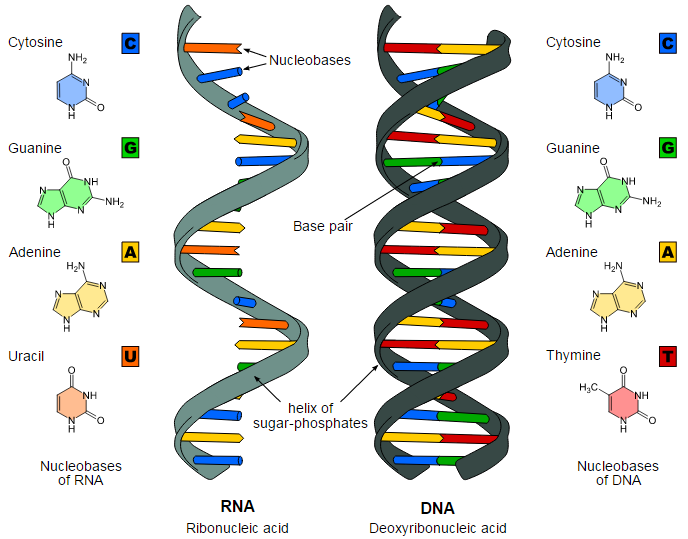
What Are The Similarities Between Dna And Rna Albert Io

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
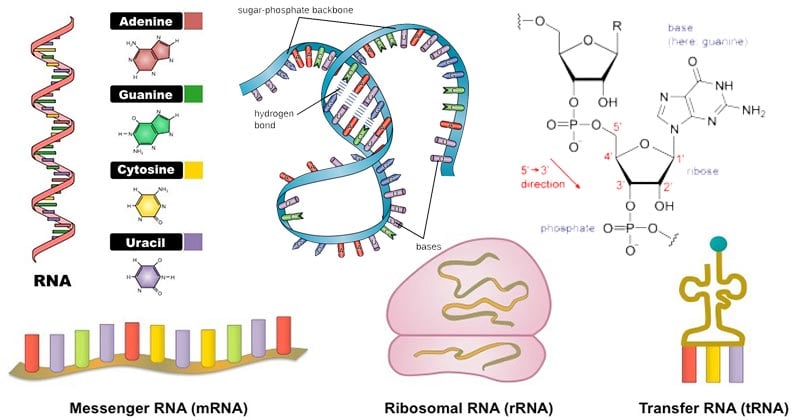
Rna Properties Structure Types And Functions

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks

Dna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
How To Show Through The Difference Of Structure Between Dna And Rna In Terms Of Sugar Portion Quora
Nucleotides Composition And Structure
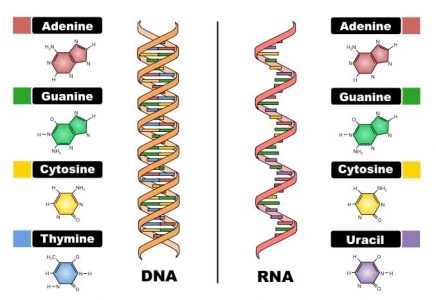
Types Of Rna And How To Extract Or Purchase It Biochain Institute Inc
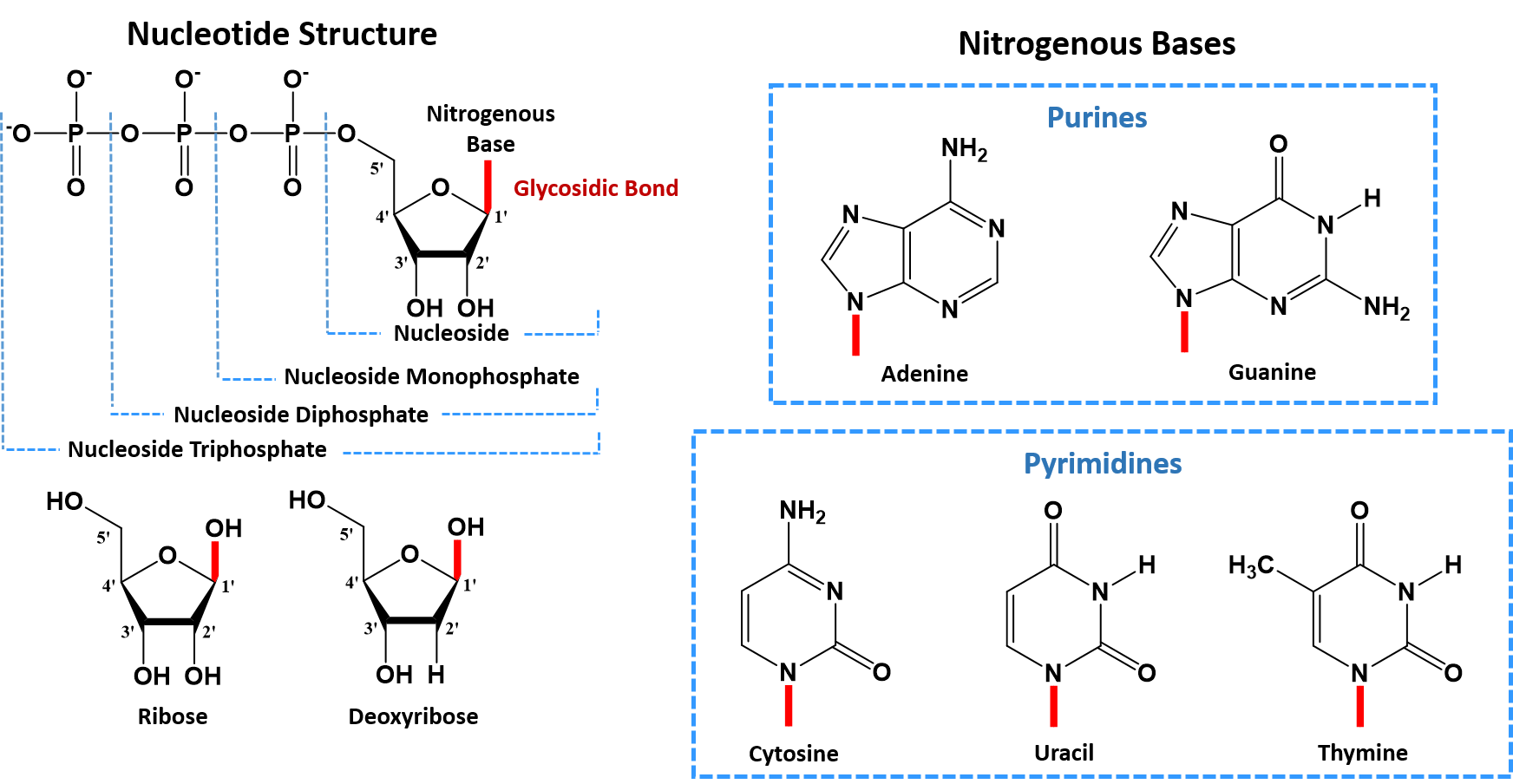
Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry
Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii

Pdf Difference Between Dna And Rna



Comments
Post a Comment